Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) are transforming how organizations operate, innovate, and compete. On their own, each technology is powerful, but together they enable intelligent automation that streamlines routine work and lets teams focus on strategic, creative tasks. From AI in IT service management (IT 서비스 관리에서의 AI) to AI-enhanced customer interactions, these tools are reshaping how businesses deliver value.
Modern organizations are using AI in cloud platforms to handle large volumes of data efficiently, while next-generation computing technologies accelerate insights and decision-making. Companies are also embracing AI for marketing optimization to better understand customer needs, and intelligent digital marketing platforms to engage audiences with personalized content. In finance, smart AI solutions are improving risk management, detecting anomalies, and enhancing investment strategies.
This guide explains how AI and RPA work together, complement each other, and can be applied to deliver faster, measurable results across IT, marketing, finance, and customer experience.
What Are RPA and AI?
AI and RPA are often mentioned in the same breath, but they are not the same thing. Understanding the difference is the first step toward designing an effective automation strategy.
Top 10 AI and RPA Contact Center Solutions for Streamlined Customer Experiences
Choosing the right platform for intelligent automation in your contact center can dramatically improve efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall business performance. Here’s a look at the top 10 AI and RPA contact center solutions to consider:
1. Bright Pattern – AI-Driven Contact Center Platform
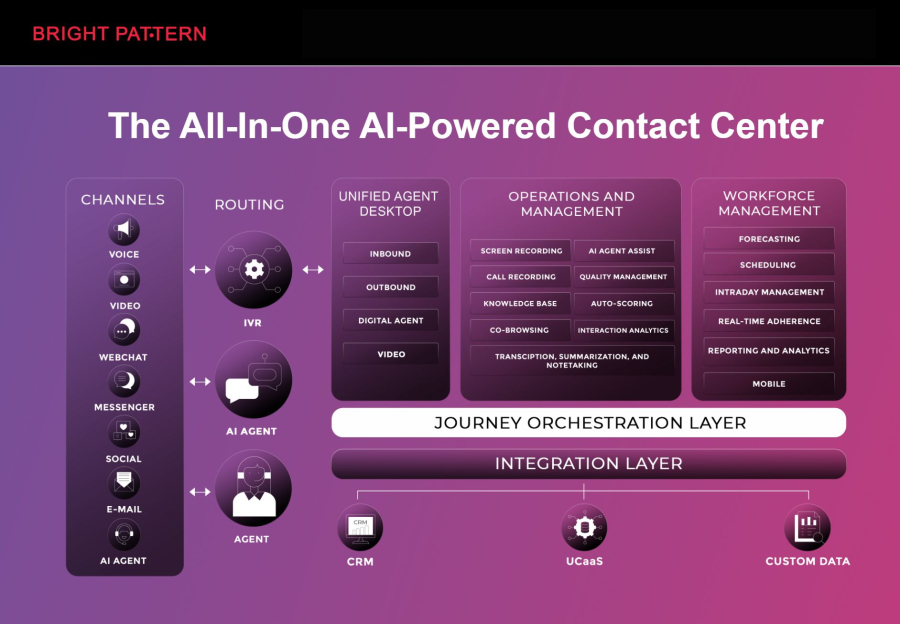
Bright Pattern leads the industry with a cloud-native contact center solution that combines AI and RPA to deliver seamless customer experiences. Their platform empowers businesses to automate repetitive tasks, integrate AI-powered chatbots, and enhance agent performance through smart routing and real-time insights.
Key features of Bright Pattern include:
- AI-assisted interactions: Agents receive real-time suggestions and guidance during customer conversations.
- Omnichannel support: Manage calls, chats, SMS, email, and social media in a single interface.
- RPA integration: Automate repetitive back-office processes for faster resolution.
- Analytics and reporting: Leverage AI-driven insights to continuously improve customer service.
- Scalable cloud deployment: Easily adapt to seasonal peaks and business growth.
Bright Pattern is ideal for businesses looking to modernize their contact centers with intelligent automation, improve agent efficiency, and deliver consistent, personalized experiences across every channel.
2. Five9
Five9 combines cloud contact center software with AI-powered automation, offering predictive dialing, intelligent routing, and virtual assistants to streamline customer interactions.
3. Genesys Cloud CX
Genesys delivers AI-driven omnichannel solutions, focusing on predictive engagement, workforce optimization, and personalized customer journeys.
4. NICE CXone
NICE CXone integrates AI and automation to optimize agent workflows, provide sentiment analysis, and enable self-service options for customers.
5. Talkdesk
Talkdesk leverages AI and RPA to offer intelligent routing, automated workflows, and real-time analytics for better customer service performance.
6. Avaya OneCloud
Avaya combines AI-driven insights and automation tools to enhance customer engagement, support hybrid workforces, and simplify contact center operations.
7. Cisco Webex Contact Center
Cisco provides AI-enabled contact center solutions with speech analytics, chatbots, and RPA to reduce operational costs and improve customer satisfaction.
8. RingCentral Contact Center
RingCentral integrates AI-driven features like predictive routing, virtual assistants, and workflow automation to optimize omnichannel experiences.
9. 8x8 Contact Center
8x8 uses AI and RPA for automated call handling, analytics, and personalized customer interactions, helping businesses scale efficiently.
10. Zendesk Sunshine
Zendesk’s AI-enhanced contact center solution supports automated ticketing, intelligent chatbots, and workflow automation for improved support experiences.
What Is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
RPAuses software robots ("bots") to mimic the actions a human takes on a computer. These bots can log into applications, click buttons, type data, copy and paste information, and move files across systems.
RPA is especially effective for processes that are:
- Rule based– The steps are clearly defined and rarely change.
- Repetitive– The same tasks are performed again and again.
- High volume– Large numbers of transactions or records are processed.
- Digital– Inputs and outputs are available in digital form.
Typical examples include invoice processing, data entry, report generation, and system reconciliations.
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
AIrefers to systems that can perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as understanding language, recognizing images, making predictions, or learning from data.
Key AI capabilities include:
- Machine learning– Models learn patterns from data to make predictions or decisions.
- Natural language processing (NLP)– Systems understand and generate human language.
- Computer vision– Systems interpret and classify images or video.
- Generative AI– Models create new content such as text, code, images, or summaries.
Where RPA follows explicit rules, AI can work withuncertainty,variation, andunstructured data, such as free‑form text or images.
How AI and RPA Complement Each Other
RPA is like a highly reliable digital worker that follows instructions perfectly, while AI is like a smart assistant that can interpret, decide, and learn.
Combine them, and you getintelligent automation:
- RPA handles structured, repetitive tasks and system interactions.
- AI handles complex perception, classification, and decision‑making.
- Together, they enable end‑to‑end automation of processes that used to require human judgment.
Why Combining AI and RPA Is So Powerful
When you add AI to RPA, you move from automating simple clicks to automating entire workflows, including steps that involve understanding language, reading documents, or making nuanced decisions.
Key benefits of AI‑powered RPA include:
1. Automating More Complex Processes
Traditional RPA works best with structured data and fixed rules. AI expands what is possible by handling:
- Unstructured documentssuch as emails, PDFs, and scanned forms.
- Variable formatswhere layouts or wording change from case to case.
- Context‑aware decisionswhere the right action depends on meaning, not just fixed rules.
As a result, processes that once needed human review can now be automated at a much higher rate, with humans focusing only on exceptions.
2. Better Accuracy and Consistency
RPA bots excel at executing the same steps exactly the same way every time, eliminating many manual errors. AI models, once properly trained and monitored, can deliver highly consistent judgments based on data.
Together, they help organizations:
- Reduce rework and corrections.
- Improve data quality across systems.
- Standardize how decisions are made across teams and regions.
3. Faster Cycle Times and Higher Throughput
AI‑enhanced bots can work around the clock, processing large volumes of work in parallel. They can read incoming requests, classify them, and take immediate action.
This leads to:
- Faster response times for customers and internal stakeholders.
- Shorter processing cycles for tasks like approvals, onboarding, or case handling.
- Greater capacity without needing to expand headcount at the same rate as demand.
4. More Engaged, Higher‑Value Human Work
One of the most compelling benefits is how intelligent automation reshapes human work. When bots and AI handle the repetitive, rules‑based, or administrative parts of a process, people can focus on tasks that require:
- Empathy and relationship building.
- Creative problem solving and innovation.
- Strategic analysis and decision‑making.
In many organizations, teams report higher job satisfaction when tedious tasks are automated and their roles evolve toward analysis, communication, and design.
5. Scalable, Repeatable Value Across the Business
Once you build a successful AI + RPA solution for one process, you can often replicate the pattern across departments and regions. Common capabilities, such as document understanding or email classification, are reusable building blocks that accelerate future automations.
This creates ascalable automation foundationthat delivers compounding value over time.
How AI‑Powered RPA Actually Works
AI and RPA can be combined in several ways. At a high level, you can think of RPA bots as the "hands" and AI services as the "brain" within a digital workforce.
Typical Architecture of Intelligent Automation
In a typical setup:
- A trigger starts the process, such as a new email, a submitted form, or a scheduled time.
- An RPA bot collects the necessary input data from systems or documents.
- An AI service analyzes that data, classifies it, or makes a prediction or recommendation.
- The bot uses the AI output to decide which path to follow and executes the remaining steps across applications.
- Exceptions or low‑confidence cases are routed to humans for review, and their decisions feed back into AI training.
Division of Roles: RPA vs. AI vs. Combined
|
Capability |
RPA Alone |
AI Alone |
AI + RPA Combined |
|
System navigation |
Clicks, types, and moves data in user interfaces. |
Not typically used for UI steps. |
Bots execute UI steps based on AI decisions. |
|
Structured data processing |
Very strong for repeatable, rules‑based tasks. |
Can analyze patterns in data. |
AI detects patterns; bots complete transactions. |
|
Unstructured text (emails, notes) |
Limited without predefined templates. |
Understands, classifies, and extracts key fields. |
AI reads content; RPA routes and processes items. |
|
Images and scanned documents |
Requires external tools to interpret content. |
Uses OCR and vision to interpret images. |
AI extracts data; RPA applies it in systems. |
|
Decision‑making |
Based on fixed rules and conditions. |
Based on learned patterns and probabilities. |
AI recommends; RPA enforces business rules and actions. |
High‑Value Use Cases for AI and RPA
AI‑driven RPA can create value in almost every industry. Below are some of the most common and impactful use cases.
1. Finance and Accounting
- Invoice processing– AI reads PDFs or scanned invoices, extracts key fields, and RPA bots match them to purchase orders and update financial systems.
- Expense management– AI interprets receipts and categorizes expenses, while RPA applies policy rules and posts transactions.
- Account reconciliations– Bots gather data from multiple systems, and AI flags inconsistencies or unusual patterns for review.
2. Customer Service and Support
- Email triage and routing– AI analyzes incoming messages, determines intent, and RPA creates or updates tickets in service tools.
- Knowledge‑powered responses– AI suggests responses or next steps, while bots fetch account information and execute changes requested by customers.
- Case prioritization– AI scores cases based on urgency or impact, and bots route them to the right teams with the right priority.
3. Human Resources (HR)
- Employee onboarding– RPA sets up user accounts and accesses in systems, while AI checks documents, extracts data, or answers common questions.
- Document handling– AI reads contracts or forms and classifies them; bots store and update records in HR systems.
- Employee support– AI assistants answer policy questions, while bots handle transactional updates like address changes or leave balances.
4. Insurance and Claims Processing
- First notice of loss (FNOL)– AI understands emails or forms describing incidents, extracts key details, and bots create claims in core systems.
- Document review– AI analyzes photos or medical reports; RPA updates claim files and calculates payments based on rules.
- Fraud analytics support– AI highlights suspicious patterns; bots pull supporting data for investigation.
5. Healthcare and Life Sciences
- Patient intake– AI reads referral letters or intake forms; RPA registers patients and schedules appointments.
- Revenue cycle management– AI validates coding or identifies missing information; bots update billing systems and submit claims.
- Regulatory and quality documentation– Bots gather required information while AI checks for missing or inconsistent data.
Realistic Success Patterns With AI and RPA
Organizations that succeed with intelligent automation tend to follow certain patterns, regardless of size or industry:
- They start withprocesses that are already somewhat standardizedand then enhance them with AI where variation is high.
- They buildsmall, high‑impact pilotsto prove value and refine their approach before scaling.
- They invest inchange management and upskilling, helping employees learn to design, manage, and collaborate with digital workers.
- They establishgovernanceto ensure automations remain reliable, secure, and aligned with business goals.
Getting Started With AI and RPA: A Practical Roadmap
You do not need to automate everything at once to see value. A focused, phased approach lets you build momentum while managing risk.
Step 1: Define Your Objectives
Begin by clarifying what you want to achieve. Common goals include:
- Reducing processing times for a specific workflow.
- Improving accuracy and compliance in a regulated process.
- Freeing up employee time for more strategic work.
- Enhancing customer or employee experience.
Clear objectives make it easier to prioritize use cases and measure success.
Step 2: Identify High‑Potential Processes
Look for processes that combine the strengths of AI and RPA, such as:
- High volume with repetitive steps that currently require manual entry.
- Frequent use of unstructured inputs like emails or attachments.
- Clear business rules combined with decisions that rely on data patterns.
It often helps to map the process end to end, then highlight where AI (perception or decision) and RPA (execution) can plug in.
Step 3: Choose the Right Tools and Skills
Many technology platforms now offer both RPA and AI capabilities, or easy integration between them. When selecting tools, consider:
- Compatibility with your existing systems and security standards.
- Availability ofprebuilt AI modelsfor tasks like document understanding or language analysis.
- Low‑code or no‑code features that allow business users to participate in design.
- Monitoring, logging, and governance features to keep automations under control.
On the skills side, cross‑functional teams that combine process experts, automation specialists, data professionals, and change leaders tend to get the best results.
Step 4: Design With Humans in the Loop
AI models are powerful but not infallible. Designinghuman‑in‑the‑loopworkflows helps you balance automation with oversight:
- Set confidence thresholds where high‑confidence AI decisions go straight through, and lower‑confidence cases go to humans.
- Capture the actions human reviewers take so they can be used to improve AI models.
- Provide clear interfaces for employees to override or adjust automation outcomes when needed.
This approach builds trust and allows you to expand automation coverage gradually as performance improves.
Step 5: Pilot, Measure, and Iterate
Start with a well‑scoped pilot process and define metrics before you go live. Useful measures include:
- Average handling time before and after automation.
- Volume of work processed per day or per week.
- Percentage of cases fully automated versus those requiring human review.
- Error rates or rework rates.
- Employee and customer satisfaction feedback.
Use what you learn to refine the solution, then apply those lessons as you roll out automation to additional processes.
Measuring the Value of Intelligent Automation
To sustain investment and enthusiasm, it is important to track the impact of AI and RPA in a structured way.
Operational Metrics
- Cycle time reduction– How much faster processes run end to end.
- Throughput increase– How much more work is processed with the same or fewer resources.
- Automation coverage– The percentage of steps or cases handled without manual intervention.
Quality and Compliance Metrics
- Error reduction– Fewer data entry mistakes or missed steps.
- Consistency– Uniform application of rules and policies.
- Auditability– Clear logs of actions taken by bots and AI components.
Human and Experience Metrics
- Employee satisfaction– Feedback on job content and workload after automation.
- Customer satisfaction– Faster responses and fewer handoffs improving experience.
- Time redeployed to higher‑value work– Hours per week that teams can now spend on analysis, improvement, or innovation.
Future Trends: Where AI and RPA Are Heading
AI and RPA continue to evolve rapidly, opening up even more possibilities for intelligent automation.
1. More Accessible, Low‑Code Intelligent Automation
Low‑code tools are making it easier for business users to design and manage automations without deep programming skills. When combined with prebuilt AI capabilities, this democratizes automation and accelerates innovation.
2. Generative AI as a Co‑Pilot for Automation
Generative AI can help teams design and maintain automations by:
- Describing processes in natural language and generating draft workflows.
- Creating or updating documentation and test cases.
- Summarizing logs and suggesting improvements to bots or models.
This turns AI into a powerful co‑pilot for both building and operating RPA solutions.
3. Closer Integration With Core Business Platforms
Enterprise software vendors increasingly embed automation and AI directly into their platforms. This means organizations can combine native capabilities with standalone RPA and AI tools, creating unified, end‑to‑end experiences.
4. From Task Automation to Process and Journey Optimization
The focus is shifting from automating individual tasks to optimizing entire processes and customer journeys. AI analyzes process data to identify bottlenecks, suggest improvements, and help you redesign workflows for maximum impact.
Building a Positive, Human‑Centric Automation Strategy
AI and RPA are at their best when they augment people, not replace them. A human‑centric approach unlocks both performance gains and stronger engagement.
Consider the following principles as you scale intelligent automation:
- Involve employees early– Invite front‑line experts to help identify opportunities, design automations, and define quality standards.
- Invest in new skills– Offer training on process design, data literacy, automation tools, and change leadership.
- Celebrate success stories– Share examples of teams who are using automation to eliminate pain points and create new value.
- Continuously improve– Treat automation as an evolving capability, not a one‑time project.
Conclusion: Turning AI and RPA Into a Strategic Advantage
AI and RPA together form a powerful foundation for intelligent automation. RPA brings speed, consistency, and integration across systems, while AI adds perception, understanding, and data‑driven decision‑making.
By combining these strengths, organizations can:
- Automate more complex, end‑to‑end processes.
- Boost efficiency and accuracy across the business.
- Elevate the work people do every day, moving them from repetitive tasks to strategic contributions.
With a clear vision, thoughtful design, and a human‑centric mindset, AI‑powered RPA can become a lasting source of competitive advantage and an engine for continuous improvement.
